The night sky holds so many wonders, doesn't it? We look up, and there are countless pinpricks of light, each a distant sun, many with their own stories to tell. One star, in particular, has been catching a lot of attention lately, sparking conversations and a bit of curious speculation. This star, a really big one, has a reputation for being a bit dramatic, and people are starting to wonder about its future.
That star, of course, is Betelgeuse, and you might have heard some whispers, or maybe even seen headlines, asking a very specific question: will Betelgeuse explode in 2025? It's a rather exciting thought, isn't it, picturing a star going out with such a grand display? This giant, reddish orb in the constellation Orion has been acting a little strangely, dimming and brightening in ways that have caught the eye of sky-watchers and scientists alike. So, it's almost natural for folks to start connecting those observations with a potential, well, stellar fireworks show.
But what's the real story behind this cosmic chatter? Is there actual science pointing to a 2025 boom, or is it more of a hopeful wish from those who enjoy a good space spectacle? We're going to take a closer look at what makes Betelgeuse so special, why astronomers are keeping such a close watch on it, and what we might actually expect from this truly immense star. You know, it's just a little bit of cosmic detective work.
- Michael Consuelos Net Worth
- Richard Williams Spouse
- Magic Johnson Draft Class
- Vanessa Williams Spouse
- Who Is Central Cee Girlfriend
Table of Contents
- Betelgeuse - A Star's Life Story
- What is the "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025" Buzz All About?
- What Happens When a Star Like Betelgeuse Explodes?
- How Close Are We to Betelgeuse and What Does That Mean for "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025"?
- Can We Really Predict When Betelgeuse Will Explode?
- Watching the Skies - How Scientists Track Betelgeuse for "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025"
- What Would We See If Betelgeuse Explodes in 2025?
- The Pop Culture Connection to "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025"
Betelgeuse - A Star's Life Story
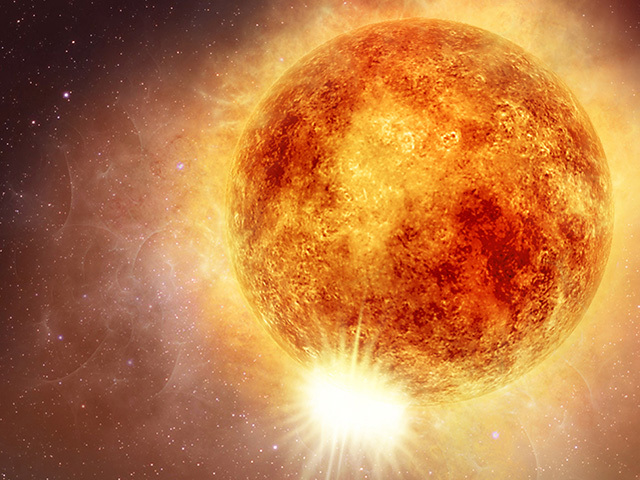
Betelgeuse, a star whose name, as we saw onscreen, is actually spelled "Betelgeuse" and not some other way, is a truly colossal object in space. It's what astronomers call a red supergiant, which basically means it's a star that's lived a very full life and is now getting ready for its grand finale. Think of it like a very old, very large tree that's shedding its leaves before its final rest. This star is so big, if you were to put it where our Sun is, its outer layers would stretch out past Mars, maybe even Jupiter. That's a truly immense size, you know, for a single celestial body.
Stars like Betelgeuse don't just hang around forever. They go through different stages, from being born in clouds of gas and dust to burning brightly for millions or even billions of years. A star's life story is, in a way, written in its mass. Smaller stars, like our Sun, tend to live for a very long time, gently fading away at the end. But the really massive ones, like Betelgeuse, live fast and die young, comparatively speaking. They burn through their fuel at an incredible rate, shining with a fiery intensity, and then, rather suddenly, they run out of steam.
When a star like Betelgeuse gets to this point, its core starts to collapse under its own immense weight. This collapse triggers an unbelievably powerful burst of energy, which we see as a supernova. It's a cosmic explosion that can briefly outshine an entire galaxy. And, as a matter of fact, Betelgeuse is expected to blow up relatively soon in astronomical terms. "Relatively soon" in this context could mean tomorrow, or it could mean a hundred thousand years from now. It's a bit like waiting for a very slow-motion, extremely bright fuse to burn down, isn't it?
- Kelly Osbourne Height
- Mr T Net Worth
- How Many Kids Does Nick Cannon Have 2024
- Steve Irwin Sayings
- Why Did Phil Spector Kill Lana Clarkson
What is the "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025" Buzz All About?
So, why is everyone talking about 2025 specifically when it comes to Betelgeuse? Well, it mostly stems from some rather noticeable changes the star went through a few years back. Around late 2019 and early 2020, Betelgeuse dimmed quite a bit, more than it usually does. This event, which some called "The Great Dimming," got a lot of people wondering if this was the big moment, the sign that the star was finally ready to go boom. Scientists looked into it, and it turned out to be caused by a massive dust cloud being thrown off the star, temporarily blocking some of its light. It was a fascinating event, to be honest, but not a direct sign of an immediate explosion.
However, once the idea of Betelgeuse exploding was out there in the public imagination, it sort of took on a life of its own. People began to speculate, and some picked a date, like 2025, to attach to this exciting possibility. It's a bit like when a rumor starts, and then everyone starts adding their own details to it. The "2025" date isn't really based on any specific scientific prediction or new observation. It's more of a popular guess, a way for people to think about something truly grand happening in the night sky within their lifetime. We humans, you know, we really love a good story with a clear timeline.
Astronomers, on the other hand, usually speak in much broader timescales when it comes to stellar events. While they agree that Betelgeuse is certainly nearing the end of its life, and it is expected to blow up relatively soon on a cosmic scale, putting an exact year on it is simply not something they can do with current knowledge. It's like trying to predict the exact minute an old, very large tree will fall; you know it's going to happen, but the precise timing is incredibly hard to pinpoint. So, while the "will Betelgeuse explode in 2025" question is fun to think about, it's not a scientific forecast.
What Happens When a Star Like Betelgeuse Explodes?
When a star as enormous as Betelgeuse finally runs out of fuel and its core collapses, the result is a supernova. This isn't just any old explosion; it's one of the most powerful events in the entire universe. Think of it this way: for a brief period, the exploding star can release as much energy as our Sun will produce over its entire ten-billion-year lifespan. It's a truly mind-boggling amount of energy, actually. The outer layers of the star are then blasted away into space at incredible speeds, creating a beautiful, expanding cloud of gas and dust that can be seen for thousands of years.
The core that remains after such a massive star explodes can become one of two things: either a super-dense neutron star or, if the original star was truly enormous, a black hole. It really depends on just how much material is left behind. This process of stellar death is incredibly important for the universe, too. These explosions scatter heavy elements, like iron, gold, and uranium, throughout space. These elements were forged inside the star's core and are now spread out, becoming the building blocks for new stars, planets, and even, well, us. So, in a way, we are all made of star stuff, literally, which is a pretty cool thought, isn't it?
A supernova is a very rare event in our galaxy, happening only a few times every century, on average. The last one visible to the naked eye from Earth happened in 1604, observed by Johannes Kepler. So, if Betelgeuse were to go supernova, it would be a truly historic event for anyone alive to witness it. It would be a bright beacon in the night sky, a sign of the universe's powerful and beautiful cycles of creation and destruction. And that, in itself, is something to really think about.
How Close Are We to Betelgeuse and What Does That Mean for "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025"?
Betelgeuse is located roughly 640 light-years away from us. Now, 640 light-years sounds like a lot, and it is. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, which is about 5.88 trillion miles. So, 640 light-years means that the light we see from Betelgeuse tonight actually left the star 640 years ago. If Betelgeuse were to explode right now, we wouldn't know about it for another 640 years. This distance is a pretty important factor when we talk about "will Betelgeuse explode in 2025" or any other specific year.
Because of this immense distance, any effects from a Betelgeuse supernova would be pretty minimal here on Earth. While a supernova can release a lot of high-energy particles, the vast stretches of space between Betelgeuse and our solar system would really help to dilute and weaken any harmful radiation. Our atmosphere and magnetic field also offer excellent protection. So, there's no need to worry about any direct danger to life on Earth. It's not like a Hollywood movie scenario where we'd be blasted by cosmic rays. The main impact would be a truly spectacular light show, which is a rather pleasant thought.
The focus here is mainly on geography, layouts, distances and so on, between major known systems, like our own, and distant celestial objects. The fact that Betelgeuse is relatively close, in cosmic terms, but still far enough away to be safe, puts it in a unique spot. It's close enough for us to see its changes and anticipate its eventual demise, but distant enough that its explosive end won't cause us any harm. It's a rather perfect cosmic neighbor for a grand astronomical event, if you think about it.
Can We Really Predict When Betelgeuse Will Explode?
This is the big question, isn't it? Can we really put a date on something as monumental as a star exploding? The short answer, honestly, is no, not with any real precision. While scientists know that Betelgeuse is in the final stages of its life, the exact timing of its supernova is incredibly hard to pinpoint. Stars don't come with little countdown clocks. Their internal processes, while understood in broad strokes, are complex and don't give us exact dates. It's a bit like knowing an old car is going to break down soon, but not knowing if it'll be next week or next year, or even ten years from now, you know?
The "Great Dimming" event, as we talked about, really highlighted this uncertainty. For a while, some people thought it was the precursor to an explosion, but it turned out to be something else entirely. This shows how much we're still learning about these huge stars and their behaviors. They are, after all, massive balls of plasma, constantly churning and changing in ways that are sometimes unpredictable from our distant vantage point. So, while we can say "relatively soon" in astronomical terms, that could mean anything from thousands of years to, well, tomorrow. There's just no way to know for sure right now.
Scientists are always observing Betelgeuse, looking for any new clues. They study its brightness, its size, and even the gases it's throwing off. But even with all of this careful watching, predicting the exact moment of a supernova is still beyond our current capabilities. It's a bit like trying to predict the exact second a volcano will erupt when you only have distant sensors. You can see signs, but the precise moment is a mystery until it happens. So, the idea of "will Betelgeuse explode in 2025" is more of a fun speculation than a scientific forecast, honestly.
Watching the Skies - How Scientists Track Betelgeuse for "Will Betelgeuse Explode in 2025"
Even though predicting the exact date of Betelgeuse's explosion is not possible, scientists are still very much interested in this star. They use powerful telescopes, both on Earth and in space, to keep a very close eye on it. These instruments can measure the star's brightness, its temperature, and even its physical size, which can change as it goes through different phases of its life. This continuous observation helps them to better understand how these huge stars behave in their final years. They're basically gathering as much data as they can, just in case something significant happens, you know?
Astronomers also study the light coming from Betelgeuse very carefully. By breaking down the light into its different colors, they can figure out what elements are present in the star and how fast its outer layers are moving. This kind of analysis gives them clues about the star's internal processes and whether it's getting closer to its explosive end. It's a bit like a doctor doing blood tests to see how a patient is doing; the light carries
Related Resources:


Detail Author:
- Name : Ahmed Rohan
- Username : murray.price
- Email : veda89@larkin.net
- Birthdate : 1978-07-02
- Address : 88941 Mante Coves O'Connermouth, ME 07684-9218
- Phone : +1-570-973-4860
- Company : Bruen, Connelly and Hauck
- Job : Brake Machine Setter
- Bio : Possimus atque possimus enim aperiam amet omnis ipsam. Tenetur dolorem incidunt illo aperiam modi consequatur. Tempore et aliquid aperiam tempore quae. Repellat autem doloribus quia et optio.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/adelia9514
- username : adelia9514
- bio : Libero praesentium non esse amet. Temporibus ea impedit dolores.
- followers : 6112
- following : 252
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/adelia_official
- username : adelia_official
- bio : Enim eaque nihil ea perferendis culpa voluptas.
- followers : 5700
- following : 2725